记录一些必需的知识,经常更新~
类型不一致
main() {
var number = 3;
print(number);
number = 3.2;
print(number);
}运行这段代码会报错,var将变量number当成了int类型,所以不能赋值给double类型,不过可以使用num类型,因为num包括int和double。
动态类型
动态类型可以在赋值时转换。
main() {
dynamic dynamicVariable = 'A string'; // type String
print(dynamicVariable);
dynamicVariable = 5; // type int
print(dynamicVariable);
dynamicVariable = true; // type bool
print(dynamicVariable);
}const和final的区别
final可以在运行时或者编译时进行赋值,之后就不可以改变。
const只能在编译时赋值,之后不可以改变。
操作符
| Operator | Use |
|---|---|
+ | Adds two operands |
- | Subtracts the second operand from the first |
-expr | Reverses the sign of the expression (unary minus) |
* | Multiplies both operands |
/ | Divides the first operand by the second operand |
~/ | Divides the first operand by the second operand and returns an integer value |
% | Gets the remainder after division of one number by another |
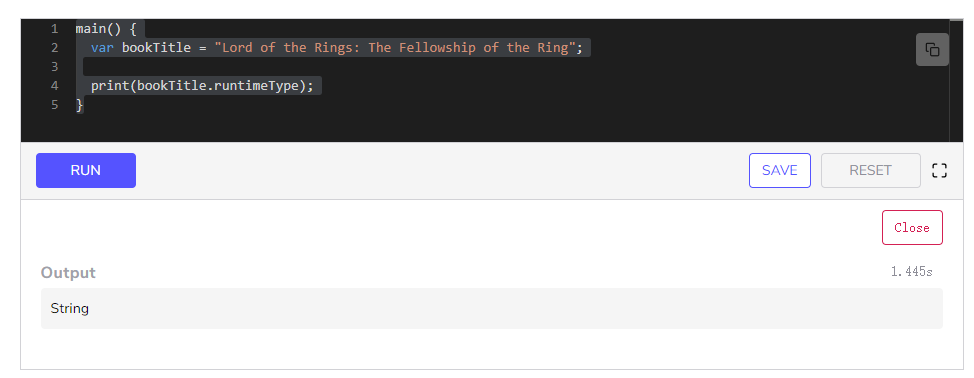
类型测试
查看运行时类型
| Operator | Use |
|---|---|
as | typecast |
is | True if the object has the specified type |
is! | False if the object has the specified type |
main() {
double type1 = 5.0;
int type2 = 87;
String type3 = "educative";
bool type4 = true;
print(type1 is int);
print(type2 is int);
print(type3 is String);
print(type4 is double);
print(type4 is! double);
}子字符串查找
Most methods allow you to only pass an argument of a specific data type. Let’s call one of Dart’s built-in methods, indexOf to get a better idea of how this works.
indexOf is called on a string and you pass it one argument of type String. It is used to calculate the starting index of a specified substring within a string.
Index is the position of an object. In Dart it always starts with 0.
三种集合类型
List Set Map
List
创建List

还可以使用构造方法

输出 [???, ???]
获得数组长度
main() {
var listOfVegetables = ['potato', 'carrot', 'cucumber'];
print(listOfVegetables.length);
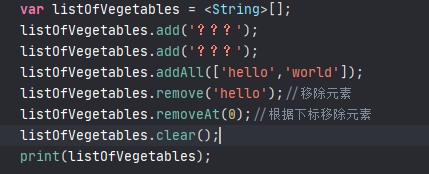
}添加多个数据
注意数据类型必须相同

移除数据

移除全部数据
使用Map方法遍历
map可以对List中的元素进行操作,操作后输出的还是List

使用toList变成List
var map=listOfVegetables.map((e) => 'I am ${e}').toList();[I am ???, I am ???, I am world]使用Set
使用Set和List类似,不过Set使用{},而List使用[]。Set是独一无二的元素。
如果想明确数据类型可以这样

main() {
var setOfFruit = <String>{};
print(setOfFruit);
Set<String> anotherSetOfFruit = {};
print(anotherSetOfFruit);
}set内是否包含某元素

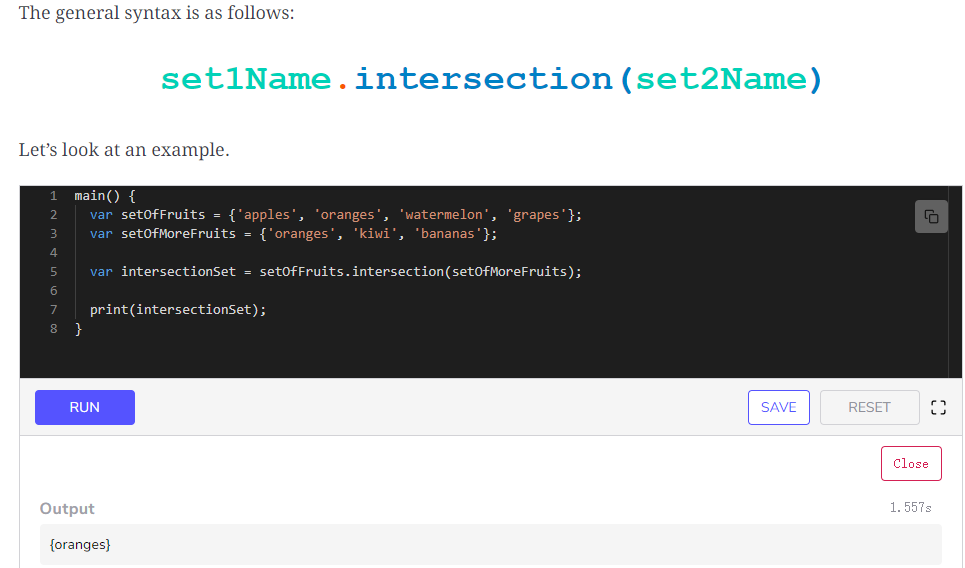
求交集
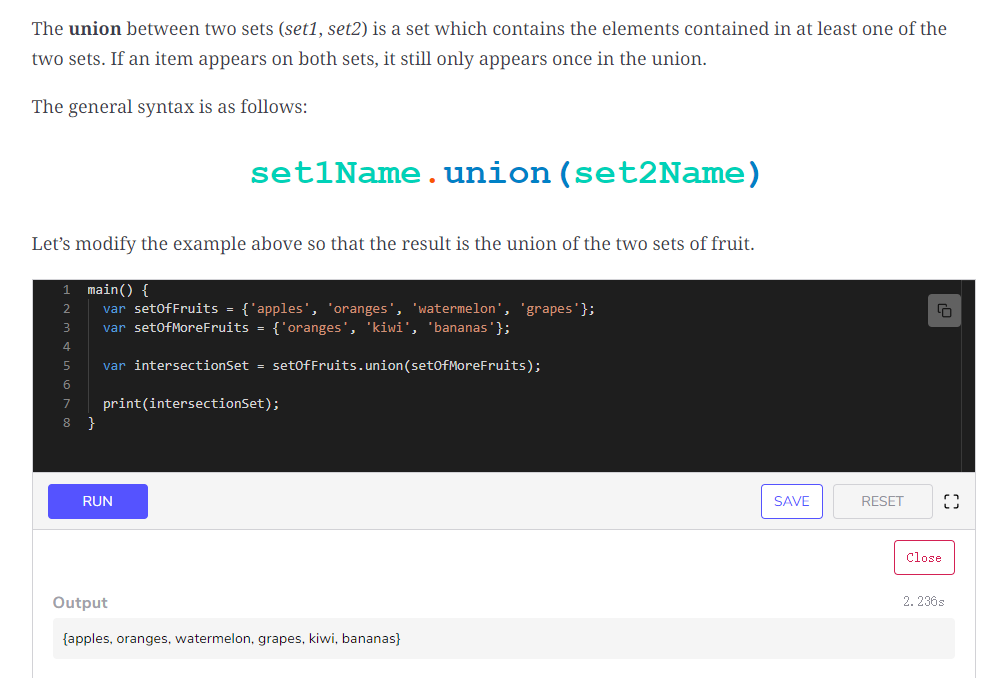
求并集
Map的使用
定义方式
import 'dart:io';
void main(List<String> arguments) {
var capitals = {
'United States': 'Washington D.C.',
'England': 'London',
'China': 'Beijing',
'Germany': 'Berlin',
'Nigeria': 'Abuja',
'Egypt': 'Cairo',
'New Zealand': 'Wellington'
};
var numbers = <int, String>{}; //map
capitals['hello'] = 'world'; //也可以使用这种方式添加键值对
print(capitals.containsKey('hello'));//是否包含某个键值对
capitals.keys;//得到key
capitals.values;//得到值
print(capitals);
}
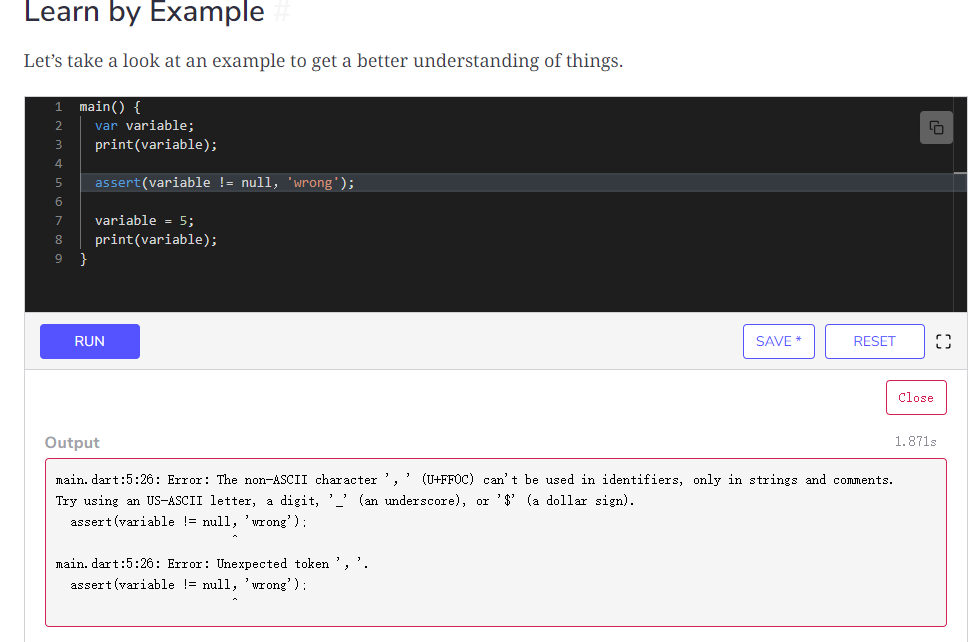
使用Assert
assert断言的作用在于当程序出现值的异常时,可以抛出。

函数
当函数只有一句时:
num sum(num x, num y) => x+y;
可选参数
使用{}时,必须指定传递参数的名字
printer(num n,{String s1, String s2}) {
print(n);
print(s1);
print(s2);
}
main() {
printer(75,s1: '1',s2: '2');
}使用[],时按照位置对应的
String mysteryMessage(String who, [String what, String where]){
var message = '$who';
if(what != null && where == null){
message = '$message said $what';
} else if (where != null){
message = '$message said $what at $where';
}
return message;
}
main() {
var result = mysteryMessage('Billy', 'howdy');
print(result);
}函数用法
函数可以当作参数
List<int> forAll(Function f, List<int> intList){
var newList = List<int>();
for(var i = 0; i < intList.length; i ++){
newList.add(f(intList[i]));
}
return newList;
}foreach
main() {
var tester = [1,2,3];
tester.forEach(print);
}void main(){
var tester = [1,2,3];
for(var name in tester){
print(name);
}
}匿名函数

main() {
var list = [1,2,3];
list.forEach((item) {
print(item*item*item);
});
}相当于
main() {
var list = [1,2,3];
list.forEach(
(item) => print(item*item*item));
}函数内定义函数
void outerFunction(){
print("Outer Function");
void nestedFunction(){
print("Nested Function");
}
nestedFunction();
}
main() {
outerFunction();
}创建一个类
可以不使用new,其它与java相同
class Person{
String name;
String gender;
int age = 0;
walking() => print('$name is walking');
talking() => print('$name is talking');
}
int main() {
// Creating an object of the Person class
var firstPerson = Person();
}构造方法
构造方法可以缩略成一句话,自定义构造方法实例:
class Person{
String name;
String gender;
int age;
// Generative Constructor
Person(this.name, this.gender, this.age);
// Named Constructor
Person.newBorn(){
this.age = 0;
}
walking() => print('$name is walking');
talking() => print('$name is talking');
}
int main() {
var firstPerson = Person("Sarah","Female",25);
var secondPerson = Person.newBorn();
print(secondPerson.age);
}Setter和Getter
注意,变量前加下划线表示私有。只有私有属性蔡恒创建setter和getter。
class Person {
String _name;
String _number;
String get name => _name;
set name(String value) {
_name = value;
}
String get number => _number;
set number(String value) {
_number = value;
}
}
动态List
List<dynamic>(表示一组由任何类型对象组成的列表)。避空运算符
Dart 提供了一系列方便的运算符用于处理可能会为空值的变量。其中一个是 ??= 赋值运算符,仅当该变量为空值时才为其赋值:
int a; // The initial value of any object is null. a ??= 3; print(a); // <-- Prints 3. a ??= 5; print(a); // <-- Still prints 3.
另外一个避空运算符是 ??,如果该运算符左边的表达式返回的是空值,则会计算并返回右边的表达式。
print(1 ?? 3); // <-- Prints 1. print(null ?? 12); // <-- Prints 12
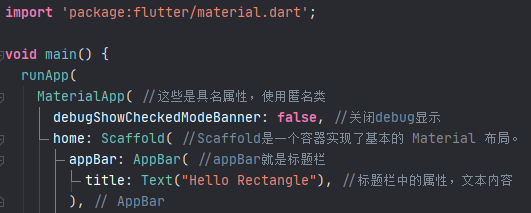
关闭Debug角标
Dart没有非零即真
必须为bool类型才可判断

构造函数初始化列表

final的对象不能写在构造方法里,使用这种方法,实现没有传值时对final的初始值

更简便的实现方法。

重定向构造函数
void main() {
print(Student(20).toString());
}
class Student {
final age;
String name;
@override
String toString() {
return 'Student{age: $age, name: $name}';
}
Student(var age):this.forname(age,'chen');
Student.forname(this.age,this.name);
}Mixin继承
void main() {
test a = test();
a.printf();
}
mixin name {
void printf() {
print('hello');
}
}
class test with name {}